课程 图形学 Animation
about 图形学中的动画效果,只讨论 Physics-Based Animation。
属于图形学系列文章。
Type of Dynamics:
- Point (particle)
- Rigid body
- Deformable body (e.g., elastic materials, fluids, smoke)
Physics-Based Animation
定义:Simulating object motion
Q:How to simulate?
A:Simulating the underlying physics
Q:What is the simulation like?
A:一般通过 (ordinary or partial) differential equations 来描述
例子:
其中:
: a moving point
: its velocity
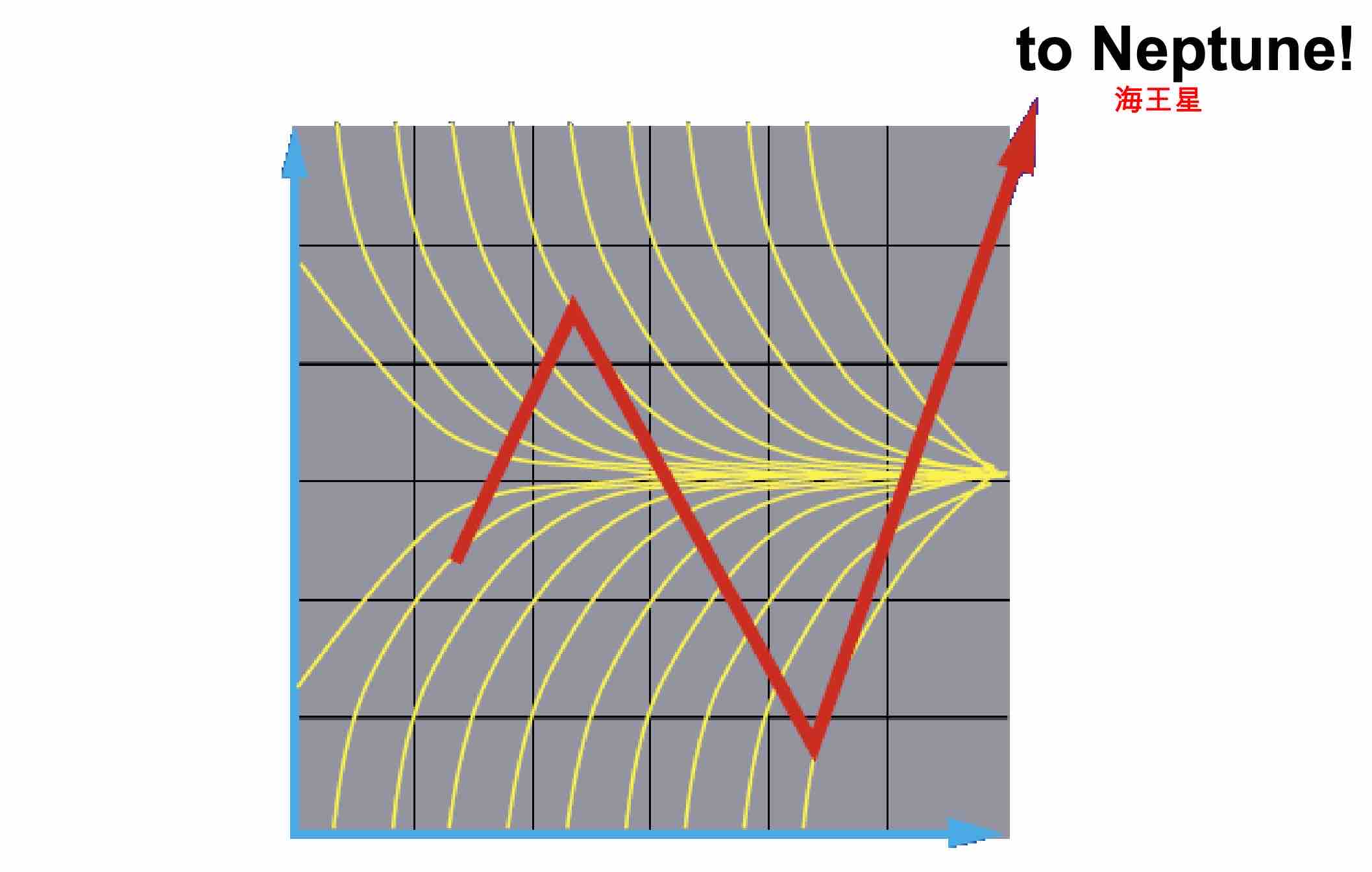
The differential equation defines a vector field over x (at any time t)
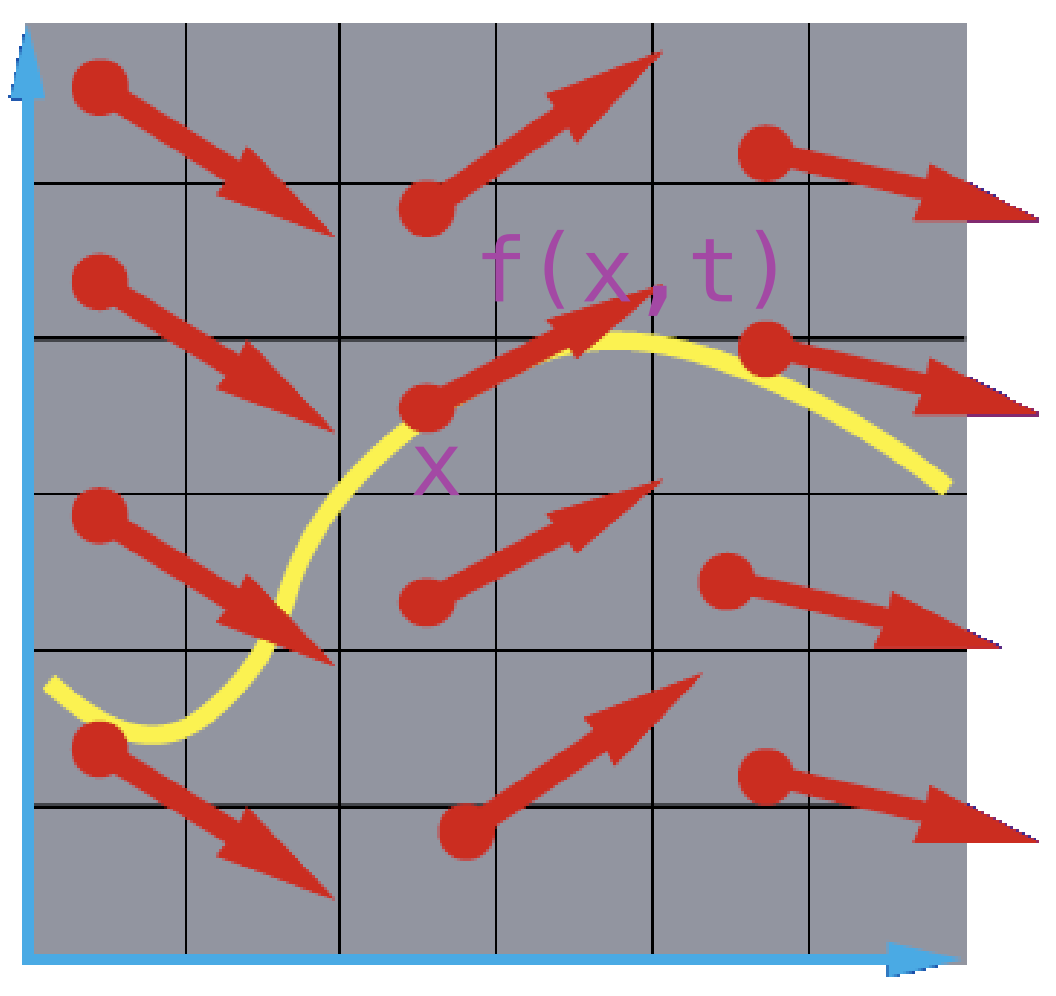
Integral Curves: 图中黄色的曲线
Initial Value Problems: 给定函数的微分方程和其中的一个点,求原函数是什么
介绍了Euler’s Method求解这个问题
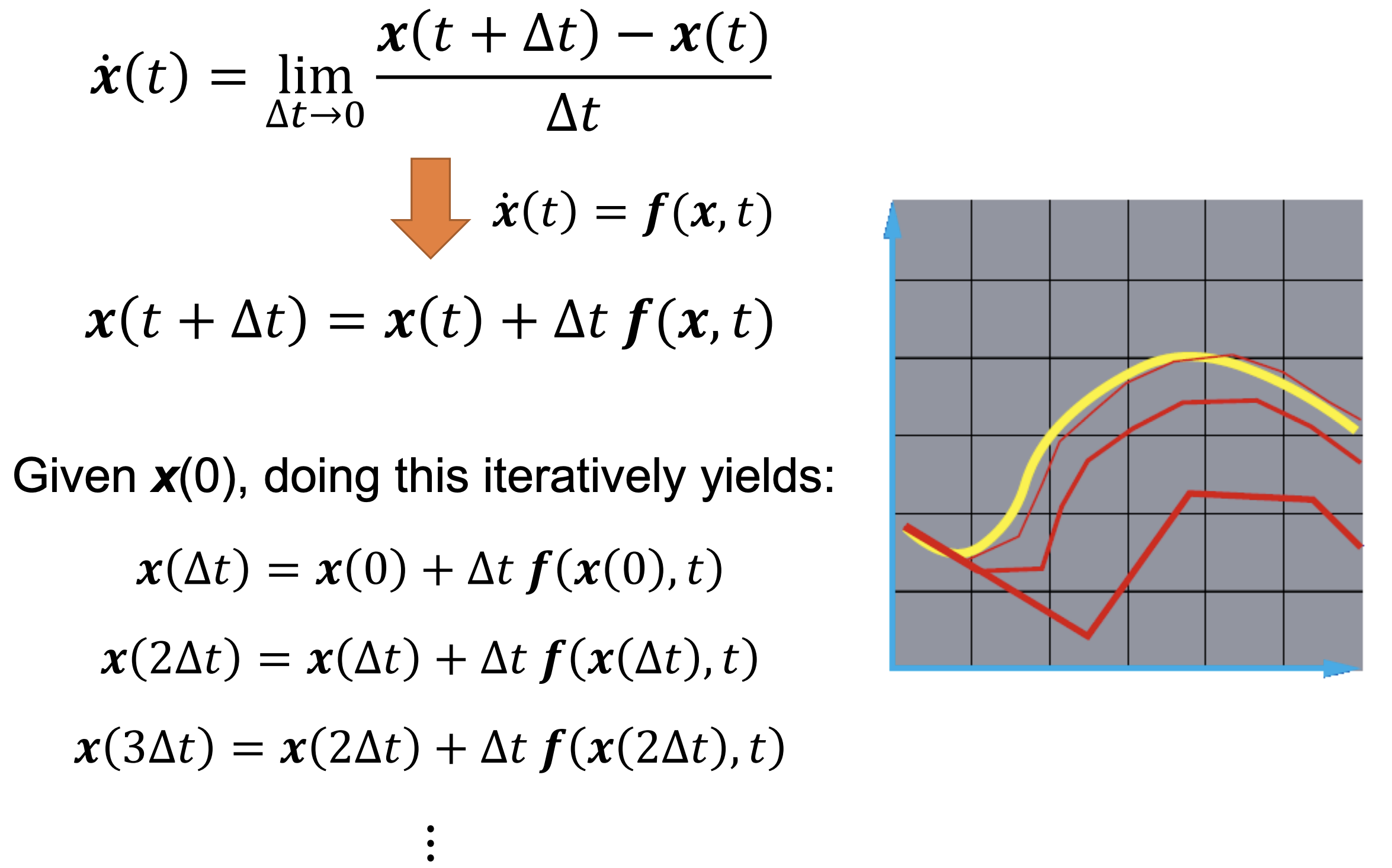
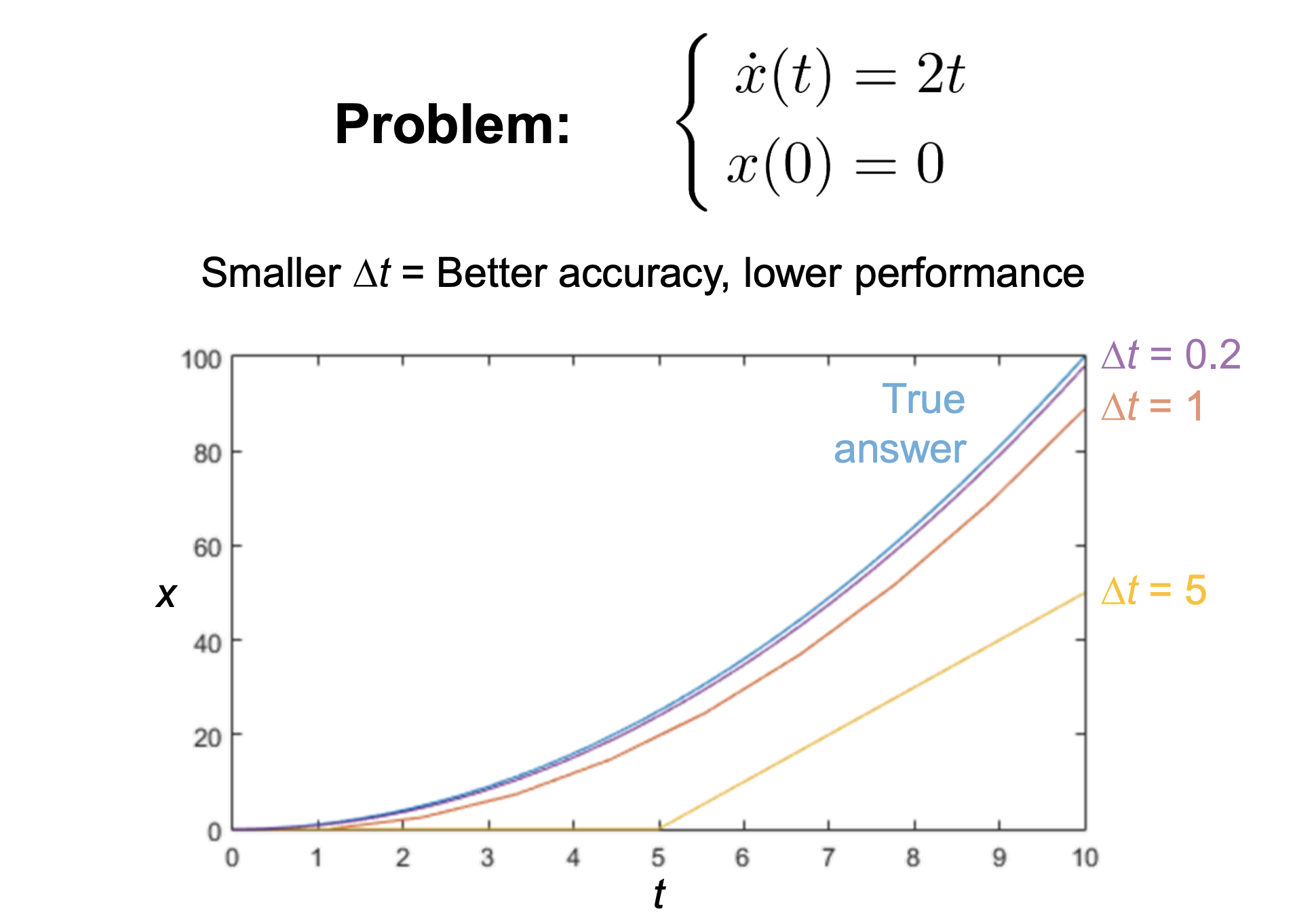
但是这方法有很多问题
Problem 1: Inaccuracy 误差会导致x(t)从一个圆圈变成有明显棱角的螺线
Problem 2: Instability 下图来自维基百科

所以我们要对欧拉方法进行修正 The Midpoint Method 推导过程见wiki
1 Compute an Euler step
2 Evaluate f at the midpoint
3 Take a step using the midpoint value
总结一下:欧拉方法是一阶的,中点法是二阶的;这两种方法都很基础,不要用欧拉法因为它很不好,更多方法见 Numerical Recipes
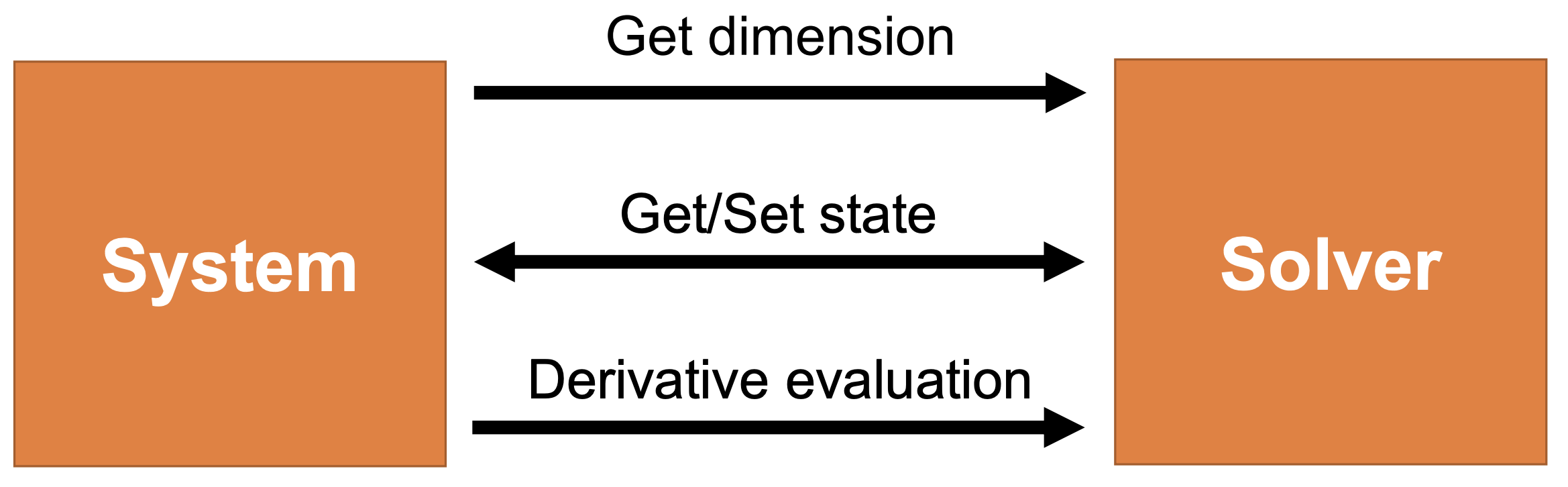
Modular Implementation
Solver Interface