课程 离散数学
复习网络安全课程时觉得很多内容与2年前上过王琦男神的离散课有重叠,然而网络安全课在数论方面写的比较简略,没办法建立一个系统的概念,于是好不容易从硬盘里找对应的课件,借此巩固一下这方面的知识。
PS:还没找到这里 md 缩小图片的方法,之前的一些操作不适用,先将就着看吧
数论部分需要掌握的: 概念: - Euler’s totient function / Euler’s Theorem - Fermat’s Little Theorem 计算: - Euclidean algorithm 算最大公约数 / Extended Euclidean algorithm - Modular Inverse (画I R T Q 表)/ 线性同余方程的解 - The Chinese Remainder Theorem (除了公式法外,还能用back substitution求解,各种回代和求逆) - The Multiplicative Order / Primitive Roots
10.10的课件主要讲算法复杂度,关系不是很大,但我老是忘记P、NP 这些复杂度的关系 (题外话:早上起来刷群消息看到新闻有一男子在南京找不到工作在地铁发病了“算法的本质和定义是什么?”hhhh CS又学疯一人)
- Polynomial-Time Algorithms O(n^k)
- n:input size of the problem
- k:a constant
- Class P -> problems that are solvable in polynomial time
- Nonpolynomial-Time Algorithms
- impractical
- class NP -> nondeterministic polynomial-time (there exists a certificate which allows one to verify in polynomial time that the input is indeed a yes-input)
- NP-Complete problems -> believed-to-be-hard decision problems in NP; they appear to have no efficient solution; answers are efficiently verifiable, solution to one is never much harder than a solution to another -> if any one of the NP-Complete problems has an efficient solution then all of the NP-Complete problems have efficient solutions
- NP-Hard problems: hardest; some of them may not be solved by a non-deterministictime. Many computational version of NP-complete problems are NP-hard.
- P = NP?
10.17和10.18的课件开始进入数论的学习
- The Division Algorithm -> 一直没搞清楚一正一负两数相除的结果,这里说是
0 ≤ r < d也就是说余数必须为正 - Congruence Relation -> 同余关系
a ≡ b (mod m)其中 m 为 modulus(模数) - Congruences of Sums and Products ->
a ≡ b (mod m) and c ≡ d (mod m) ➡ a+c ≡ b+d (mod m) and ac ≡ bd (mod m) 当m为正数时,
(a + b) mod m = ((a mod m) + (b mod m)) mod m ab mod m = ((a mod m)(b mod m)) mod mPrimes
- 不包括1
- 三个证明
- If n is composite, then n has a prime divisor less than or equal to √n.
- There are infinitely many primes.
- A prime factorization of a positive integer where the primes are in nondecreasing order is unique.
一些概念 Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)、Least Common Multiple (LCM) Mersenne Primes (Primes in form of 2^p-1)
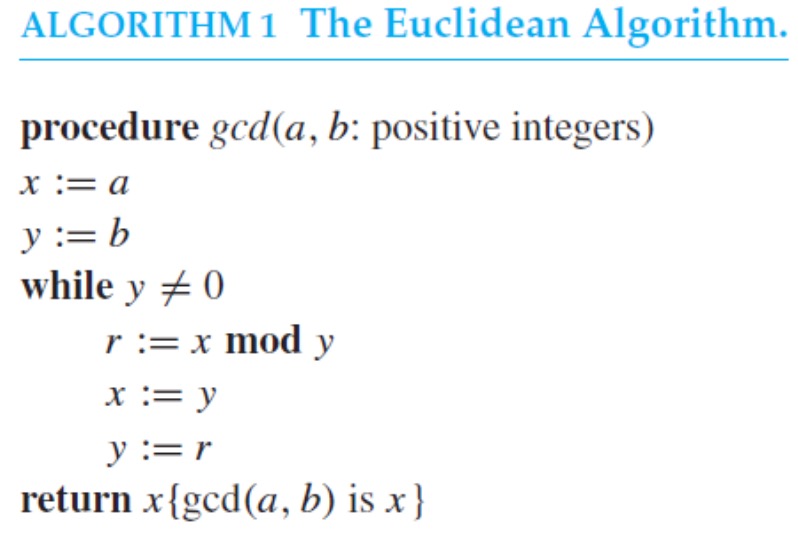
Euclidean algorithm -> 用于求解GCD,当 a >= b 时,算法复杂度为 O(log b)
Bezout’s Theorem -> If a and b are positive integers, then there exist integers
sandtsuch thatgcd(a, b) = sa + tb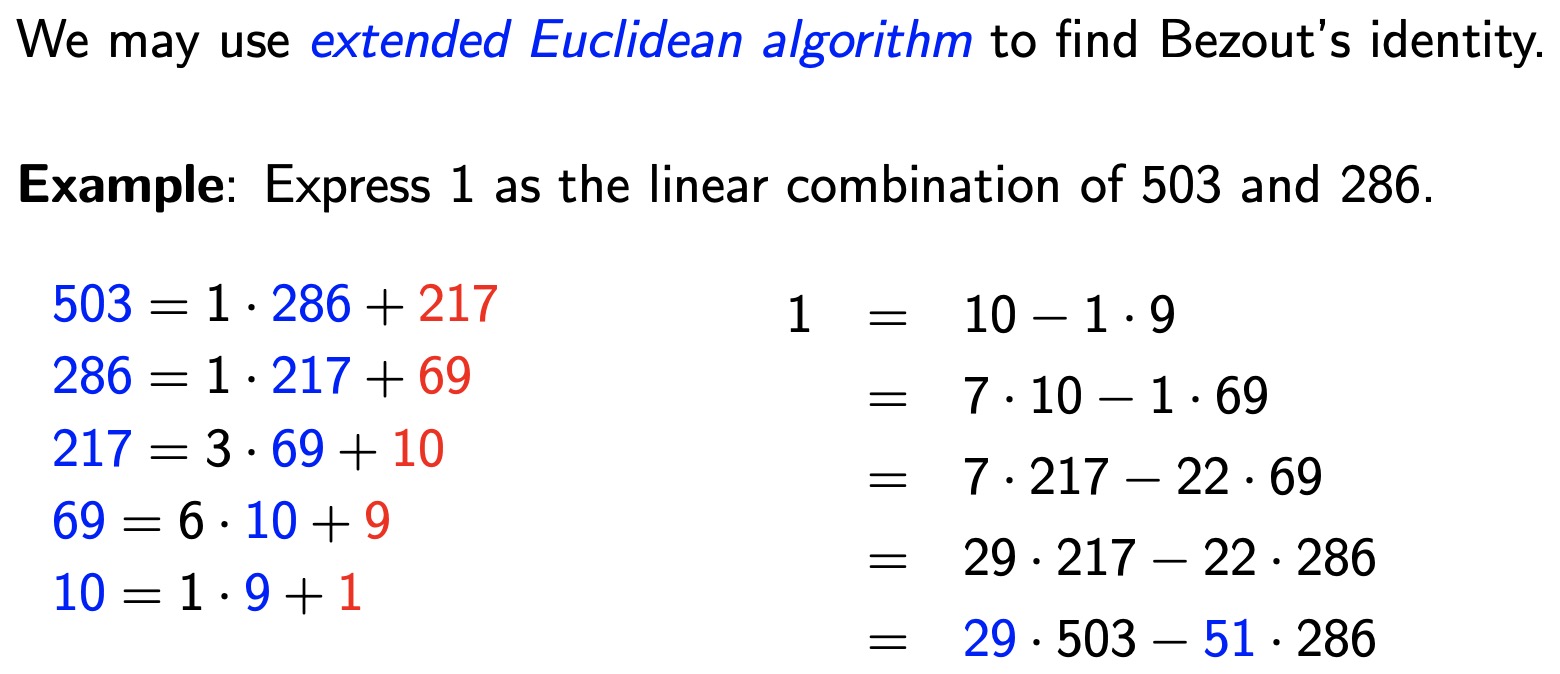
Linear Congruence 线性同余
ax ≡ b (mod m)Modular Inverse 在网络安全里面叫 multiplicative inverse
a’a ≡ 1 (mod m)通过模逆,我们可以计算出线性同余方程的解x ≡ a'b (mod m),但大前提是模逆存在Theorem: If a and m are relatively prime integers and m > 1, then an inverse of a modulo m exists. Furthermore, the inverse is uinque modulo m.
How to find inverses?
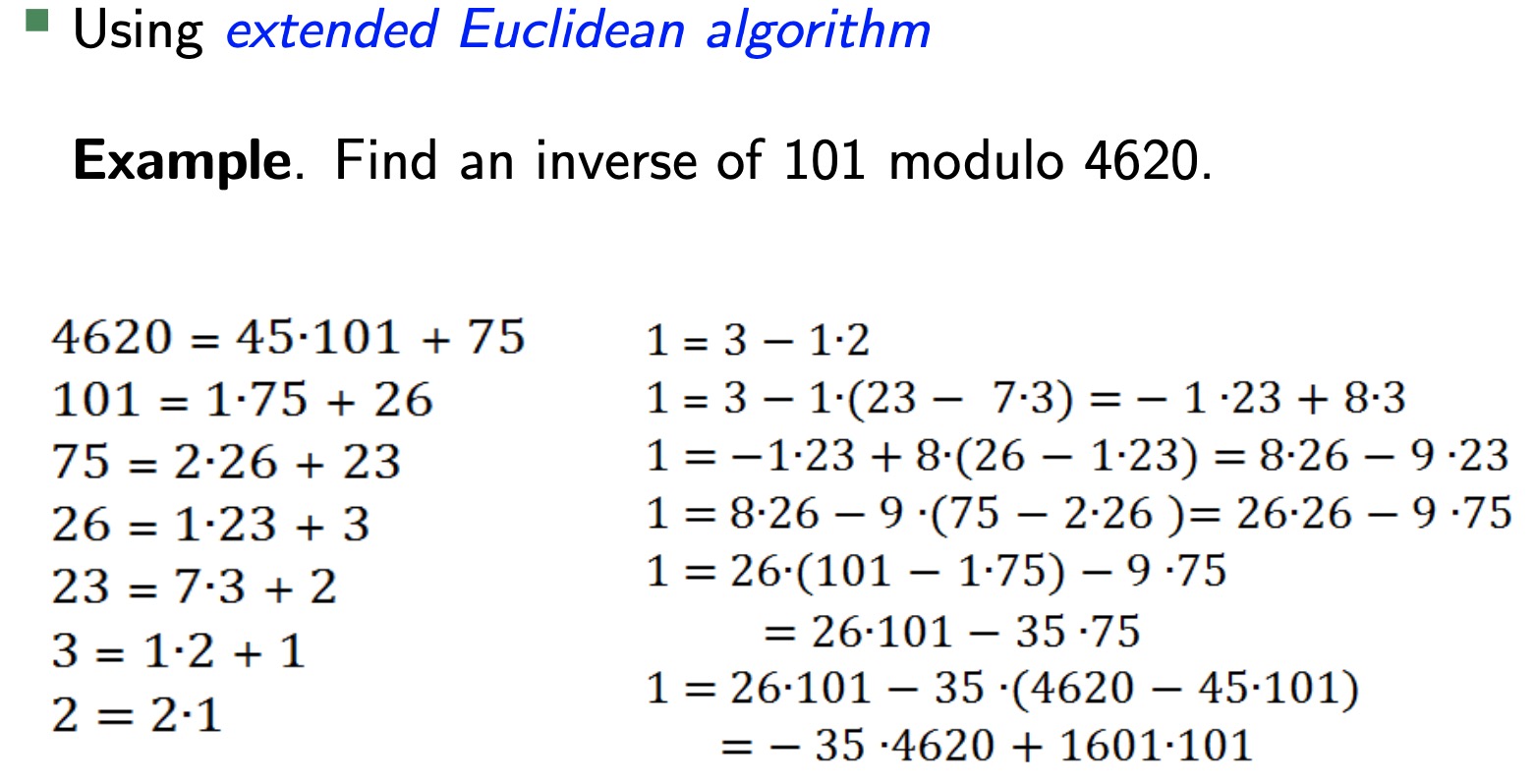

Number of Solutions to Congruences

The Chinese Remainder Theorem

 还有一种方法叫 back substitution
还有一种方法叫 back substitution

Fermat’s Little Theorem 它的证明很巧妙
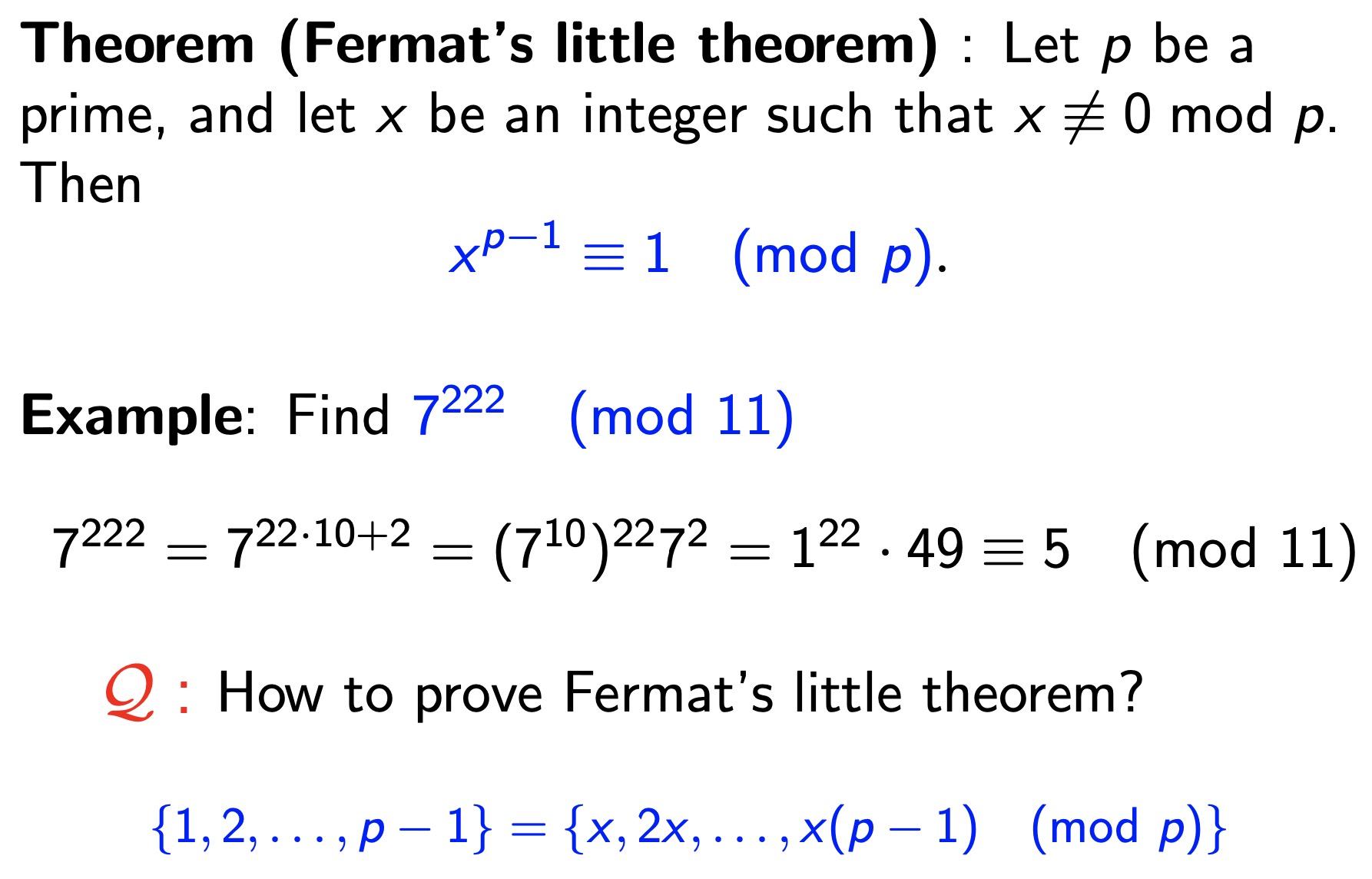
Euler’s totient function
φ(n) the number of positive integers coprime to n in Zn(第三条想了好一会才明白…p^n内为p的倍数的数应该就是
{p, 2*p, 3*p....p^(n-1)*p}好笨啊我)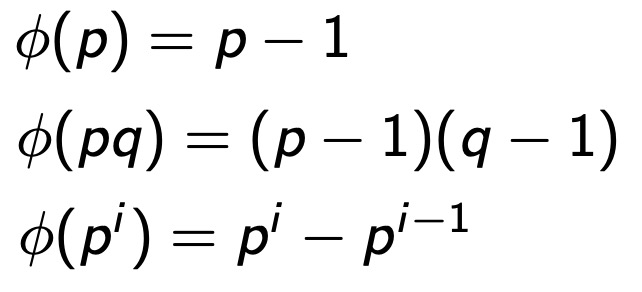
Euler’s Theorem
费马小定理的延伸和推广

The Multiplicative Order
定理是 Lagrange Theorem,其中 φ(n) 也称 order of the group,是所有 Multiplicative Order 中的最大值

Primitive Roots
若 Multiplicative Order 等于 φ(n),则被称为原根;原根的存在性在抽象代数里面相当于“有限域的乘法群是循环群”,那个原根就相当于是循环群的生成元(
想到我上一次作业天真的证明:因为质数是无穷的,所以不存在生成元)
10.24开始进入密码学的学习
Classical One-Key Ciphers

Attacks on Classical Cryptography
- Ciphertext-only attack
- Known-plaintext attack
Simple Substitution Ciphers (1-to-1 function) / Affine cipher (e.g. Caesar cipher) / Cryptanalysis
Other Symmetric Ciphers: DES / 3DES / IDEA / Blowfish Rijndael (AES)
Public-Key Cryptosystems
- W. Diffie, M. E. Hellman, “New directions in cryptography”, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, vol. 22-6, pages 644-654, 1976.
- Four properties:
- D(E(M)) = M
- Both E and D are easy to compute
- It is computationally infeasible to derive D from E
- E(D(M)) = M
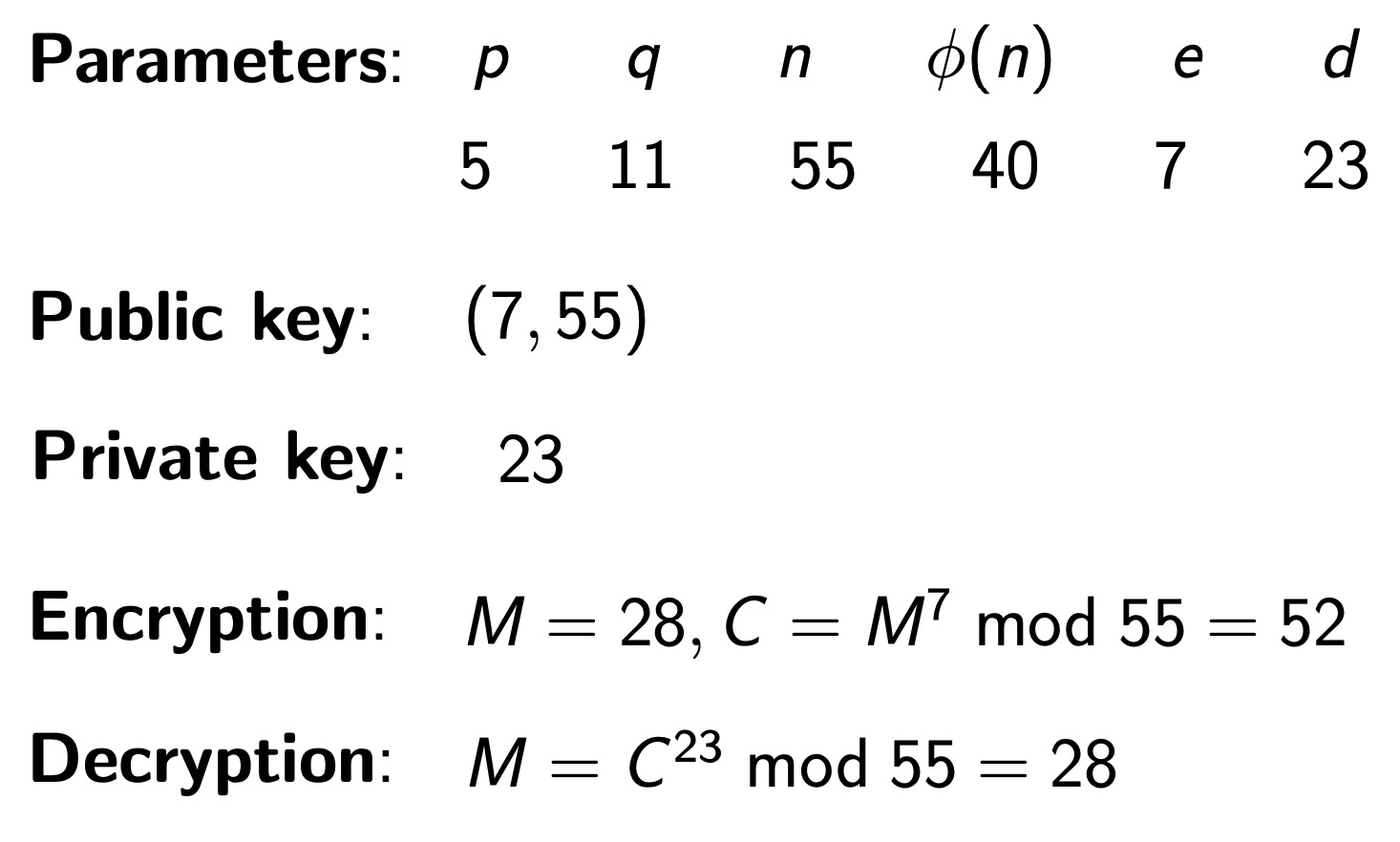
RSA Public-Key Cryptosystem
Pick two large primes, p and q. Let n = pq, then φ(n) = (p − 1)(q − 1). Encryption and decryption keys e and d are selected such that
- gcd(e, φ(n)) = 1
- ed ≡ 1 (mod φ(n))
- C = M^e mod n (RSA encryption)
- M = C^d mod n (RSA decryption)
- p, q, φ(n) must be kept secret!
原理

例子
安全性分析


RSA用于数字签名
- S = M^d mod n (RSA signature)
- M = S^e mod n (RSA verification)
The Discrete Logrithm

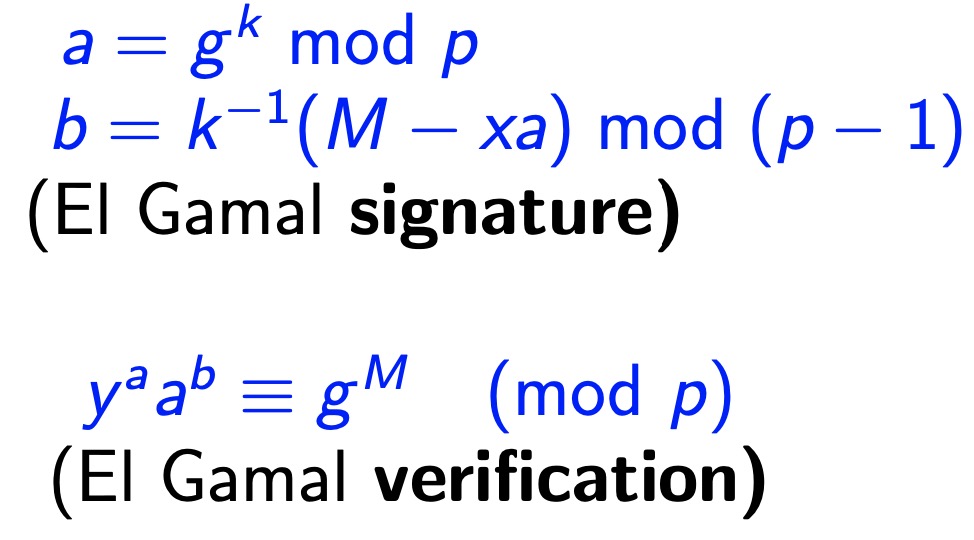
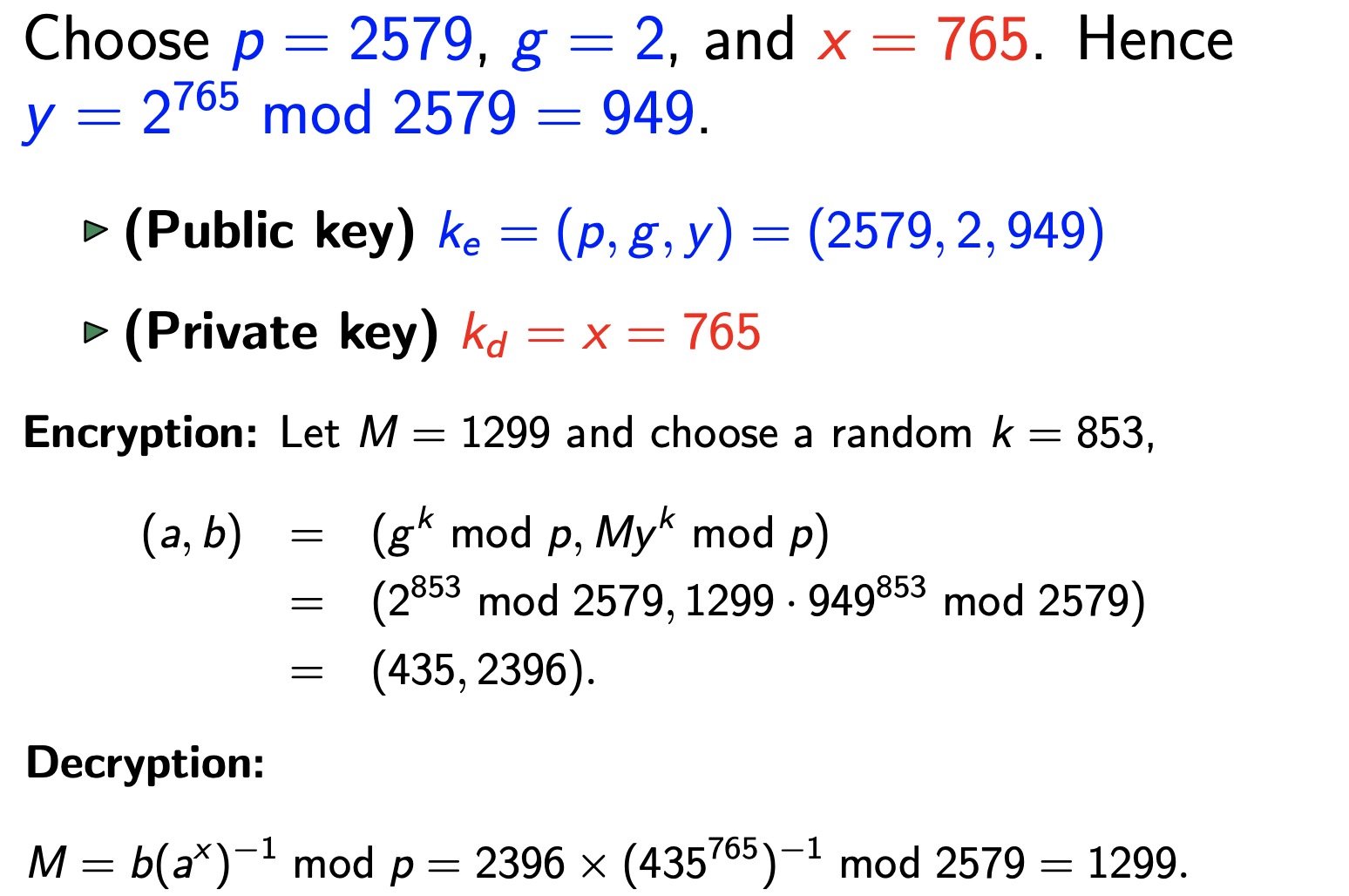
El Gamal Encryption

- El Gamal for Digital Signature
- 例子
- 安全性分析

- El Gamal for Digital Signature
Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange Protocol